
物体检测已成为一项核心创新,应用于计算机视觉、安全和身份验证措施、犯罪检测、交通、实时图像分析等多个领域。通过在网络应用程序中利用 TensorFlow 的功能,我们可以使用张量模型实现高效的物体检测。本文旨在深入介绍对象检测,并以实例说明将对象检测集成到网络应用程序中的步骤。
物体检测在各个领域的重要性怎么强调都不为过,因为它能带来诸多好处:
- 人工智能驱动的汽车:通过实施物体检测模型,自动驾驶汽车可以轻松检测并正确识别路标、交通信号灯、人和其他机车,从而有助于在驾驶过程中更好地导航和决策。
- 安全和监控:物体检测大大增强了安防系统,使监控系统能够跟踪和识别人和物,监控行为,并增强机场等公共场所的安全性。
- 医疗保健:作为医疗领域的一项应用,训练有素的模型可以识别扫描中的疾病和异常。通过这些模型,可以及时发现异常情况并采取补救措施。
- 增强视觉理解和数据表示:利用物体检测,计算机系统可以理解和解释图形数据,并以用户可以快速吸收的形式表示这些信息。
什么是物体检测?
物体检测是计算机视觉的一个要素,它利用人工智能(AI)从图像、视频和系统的视觉输入中获取有意义的信息。物体检测模型可以检测、分类和勾勒视觉输入中的物体(通常在一个边界框内),并执行或推荐该模型定义的操作。
物体检测模型主要由两个关键部分组成:视觉输入定位和物体分类。视觉输入定位涉及定位输入中的物体,并在检测到的物体周围指定一个边界框。这些边框考虑了检测到的物体的宽度、高度和位置(x 坐标和 y 坐标)。物体分类则是为检测到的物体分配标签,提供物体的上下文。
什么是 Tensorflow?
根据文档介绍,TensorFlow 是谷歌开发的一个开源机器学习框架,为计算机视觉、深度学习和自然语言处理等机器学习相关任务提供各种工具和资源。它支持多种编程语言,包括 Python 和 C++ 等流行语言,使更多用户可以使用它。利用 TensorFlow,用户可以创建在任何平台上运行的机器学习模型,如桌面、移动、网络和云应用。
设置开发环境
在本文中,我们将使用 React.js 和 TensorFlow。首先,请执行以下步骤:
- 在本地计算机上设置 React 应用程序,打开项目目录,然后继续下一步,添加 TensorFlow 依赖关系。
- 在项目根目录下打开 shell 窗口,使用以下命令安装 TensorFlow 依赖项:
npm i @tensorflow/tsfjs-backend-cpu @tensorflow/tfjs-backend-webgl @tensorflow/tfjs-converter @tensorflow/tfjs-core @tensorflow-models/coco-ssd
我们将开发一个网络应用程序,使用两种方法检测物体。第一种方法是检测上载图像中的物体,第二种方法是检测摄像头信号源中的物体。
利用上传图像进行物体检测
在本节中,我们将创建一个物体检测器,对上传的图像进行操作,以识别其中的对象。首先,创建一个组件文件夹和一个新文件 ImageDetector.js。在该文件中添加以下代码:
"use client";
import React, { useRef, useState } from "react";
import * as cocoSsd from "@tensorflow-models/coco-ssd";
import "@tensorflow/tfjs-backend-webgl";
import "@tensorflow/tfjs-backend-cpu";
const ImageDetector = () => {
// We are going to use useRef to handle image selects
const ImageSelectRef = useRef();
// Image state data
const [imageData, setImageData] = useState(null);
// Function to open image selector
const openImageSelector = () => {
if (ImageSelectRef.current) {
ImageSelectRef.current.click();
}
};
// Read the converted image
const readImage = (file) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.addEventListener("load", (e) => resolve(e.target.result));
reader.addEventListener("error", reject);
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
});
};
// To display the selected image
const onImageSelect = async (e) => {
// Convert the selected image to base64
const file = e.target.files[0];
if (file && file.type.substr(0, 5) === "image") {
console.log("image selected");
} else {
console.log("not an image");
}
const image = await readImage(file);
// Set the image data
setImageData(image);
};
return (
<div
style={{
display: "flex",
height: "100vh",
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
gap: "25px",
flexDirection: "column",
}}
>
<div
style={{
border: "1px solid black",
minWidth: "50%",
position: "relative"
}}
>
{/* Display uploaded image here */}
{
// If image data is null then display a text
!imageData ? (
<p
style={{
textAlign: "center",
padding: "250px 0",
fontSize: "20px",
}}
>
Upload an image
</p>
) : (
<img
src={imageData}
alt="uploaded image"
/>
)
}
</div>
{/* Input image file */}
<input
style={{
display: "none",
}}
type="file"
ref={ImageSelectRef}
onChange={onImageSelect}
/>
<div
style={{
padding: "10px 15px",
background: "blue",
color: "#fff",
fontSize: "48px",
hover: {
cursor: "pointer",
},
}}
>
{/* Upload image button */}
<button onClick={() => openImageSelector()}>Select an Image</button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default ImageDetector;
在上面的代码片段中,我们使用 useRef 和 FileReader 来处理图像选择。点击 “Select an Image” 按钮后,隐藏的文件输入将被触发,文件选择窗口将打开。选定的图片会转换为 base64 格式,并使用 JavaScript FileReader 在异步函数中读取。此时,imageData 状态会更新为包含所选图片,三元运算符会显示图片。
要挂载此组件,我们可以在项目目录 primary app/page.jsx 中添加并渲染它:
import ImageDetector from "@/components/imagedetector";
export default function Home() {
return (
<div>
<ImageDetector />
</div>
);
}
如果我们运行应用程序,会得到如下结果:

创建图像对象检测器
为了处理所选图像中的物体检测,我们将创建一个新函数,使用我们之前安装的 TensorFlow Coco-ssd 物体检测模型:
//...
// Function to detect objects in the image
const handleObjectDetection = async (imageElement) => {
// load the model
const model = await cocoSsd.load();
// Detect objects in the image
const predictions = await model.detect(imageElement, 5);
console.log("Predictions: ", predictions);
};
上述代码使用 cocoSsd 软件包来处理对象检测。我们还将检测次数限制为 5 次,因为如果运行系统的 GPU 和 CPU 内存不足,在浏览器上运行多次检测有时会导致速度变慢。
要创建 imageElement,我们将在 onImageSelect 函数中创建一个元素,并将所选图片的数据传递给它。
// Within the onImageSelect function
//...
// Create an image element
const imageElement = document.createElement("img");
imageElement.src = image;
imageElement.onload = async () => {
handleObjectDetection(imageElement);
};
handleObjectDetection 函数返回的 predictions 结果会对所选图像中的物体进行分类,并提供有关其位置的信息。利用这些信息,我们将构建一个边界框。例如,我们可以添加一张狗和一只猫的图片,并得到以下结果:
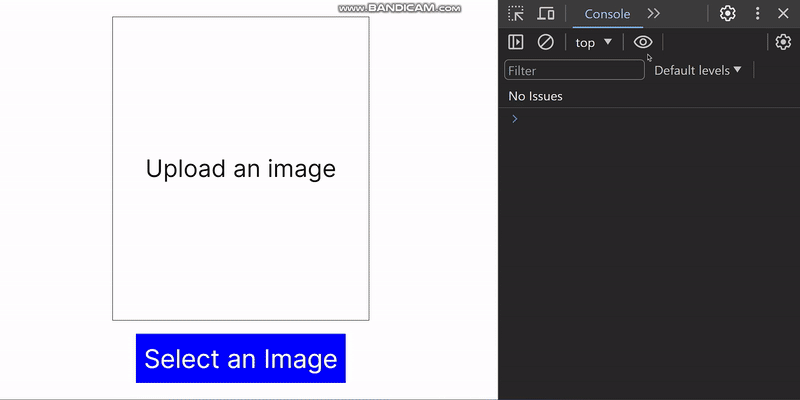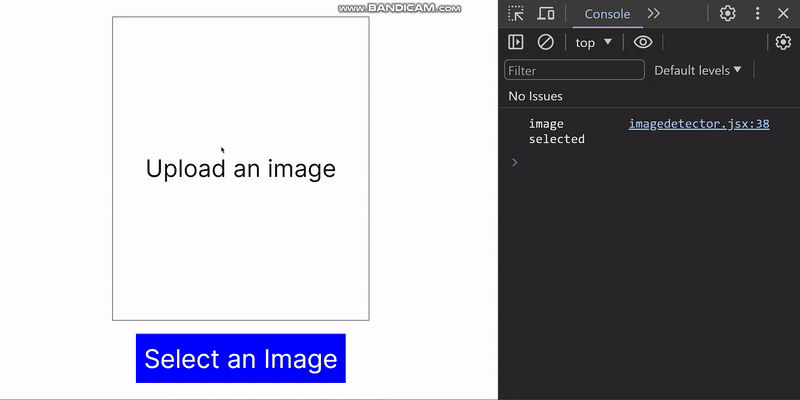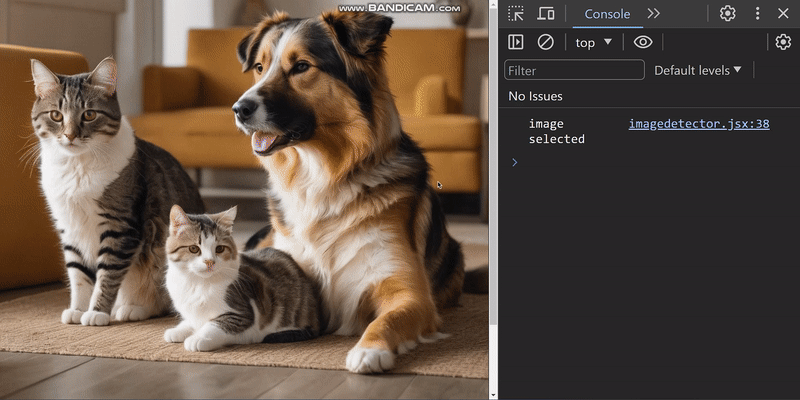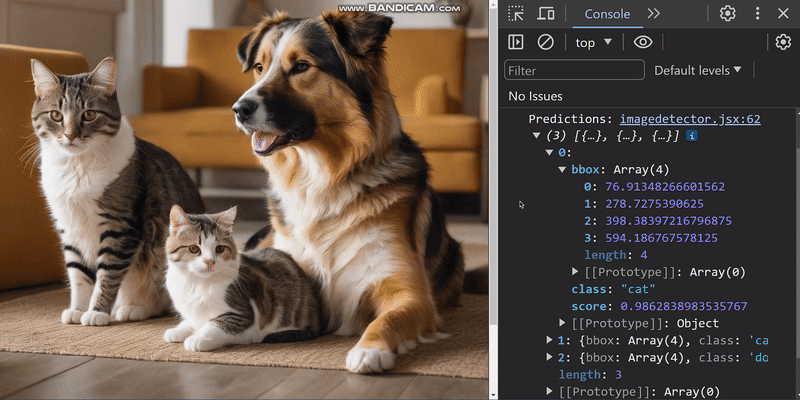
下图显示了浏览器控制台中记录的预测结果:
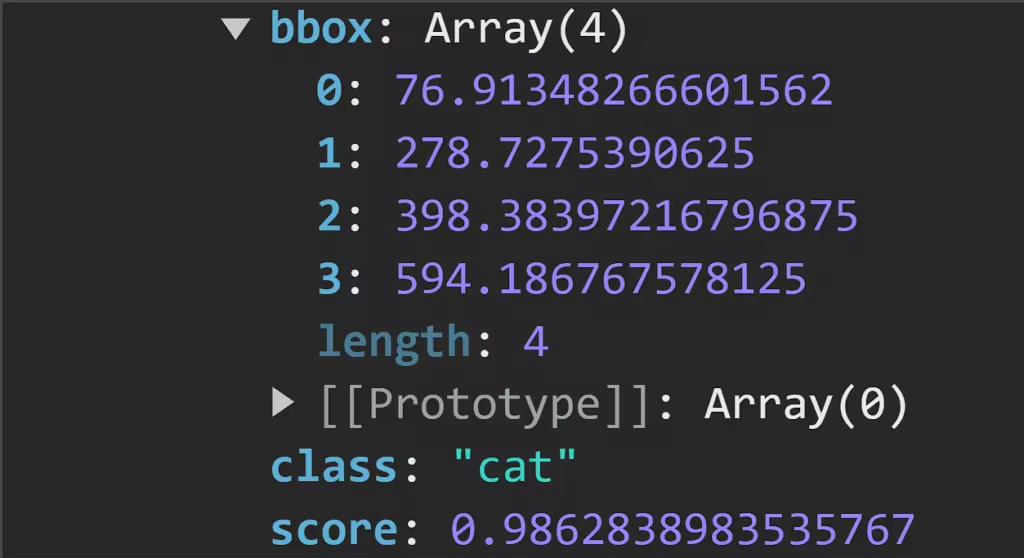
仔细观察,我们可以看到物体检测模型生成的预测结果。
- bbox:提供有关边界框位置和大小的信息。
- class:这是图像中物体的分类。
- score:预测准确度的估计值。该值越接近 1,表示预测越准确。
为预测对象构建边界框
对于预测,我们将创建一个状态对象,该对象将根据模型返回的预测数据进行更新。
// Handle predictions const [predictionsData, setPredictionsData] = useState([]);
要使用预测数据更新此状态,请对 handleObjectDetection 进行以下更改:
// Set the predictions data setPredictionsData(predictions);
我们将使用 predictionsData 数组创建一个函数,为图像中的每个元素生成一个边框。要创建独特颜色的边界框,我们首先要创建一个颜色数组和一个函数,以对数组进行洗牌并提供独特的颜色部分:
// An array of bounding box colors
const colors = ["blue", "green", "red", "purple", "orange"];
// Shuffle the array to randomize the color selection
function shuffleArray(array) {
for (let i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
[array[i], array[j]] = [array[j], array[i]];
}
}
shuffleArray(colors);
最后,我们可以用下面几行代码创建并显示边界框:
{/* Create bounding box */}
{
// If predictions data is not null then display the bounding box
// Each box has a unique color
predictionsData.length > 0 &&
predictionsData.map((prediction, index) => {
const selectedColor = colors.pop(); // Get the last color from the array and remove it
return (
<div
key={index}
style={{
position: "absolute",
top: prediction.bbox[1],
left: prediction.bbox[0],
width: prediction.bbox[2],
height: prediction.bbox[3],
border: `2px solid ${selectedColor}`,
display: "flex",
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
flexDirection: "column",
}}
>
<p
style={{
background: selectedColor,
color: "#fff",
padding: "10px 15px",
fontSize: "20px",
textTransform: "capitalize",
}}
>
{prediction.class}
</p>
<p
style={{
background: selectedColor,
color: "#fff",
padding: "10px 15px",
fontSize: "20px",
textTransform: "capitalize",
}}
>
{Math.round(parseFloat(prediction.score) * 100)}%
</p>
</div>
);
})
}
{/* Display uploaded image here */}
//... Other code below
在浏览器中,我们可以看到以下结果:
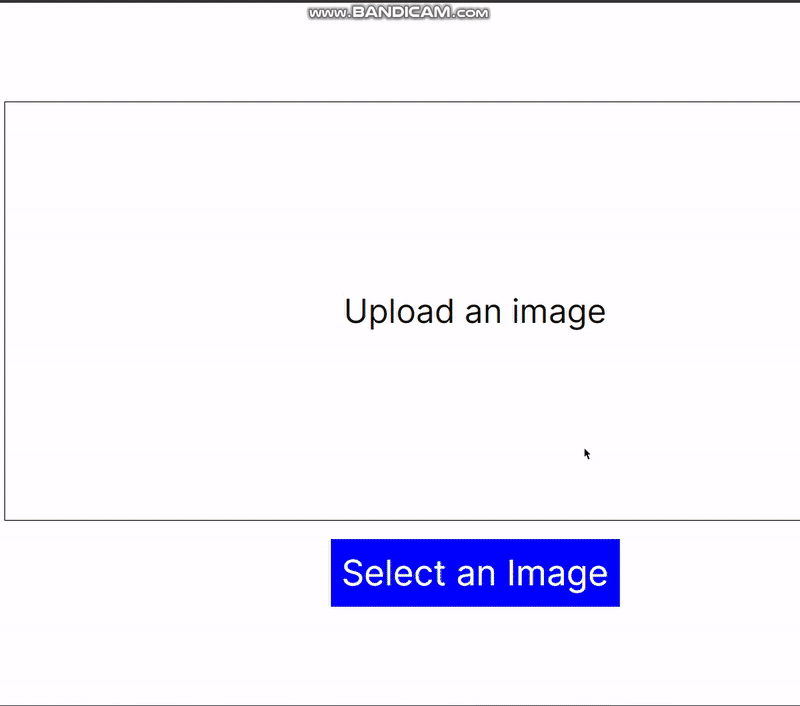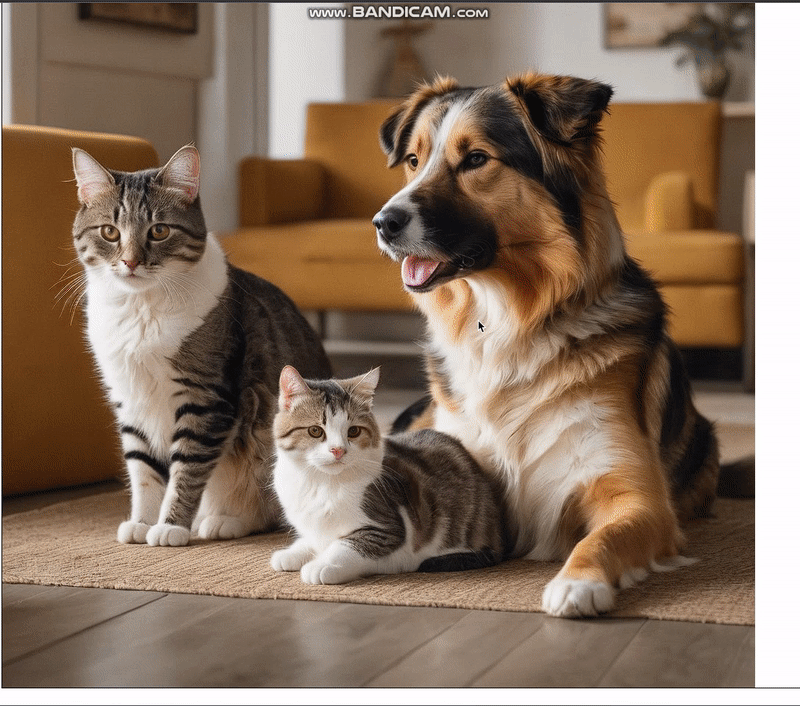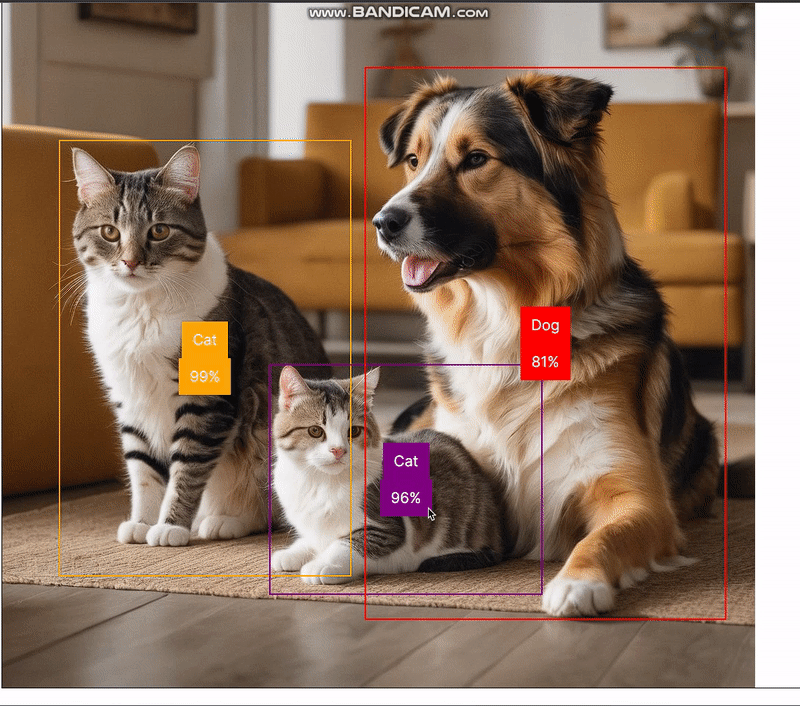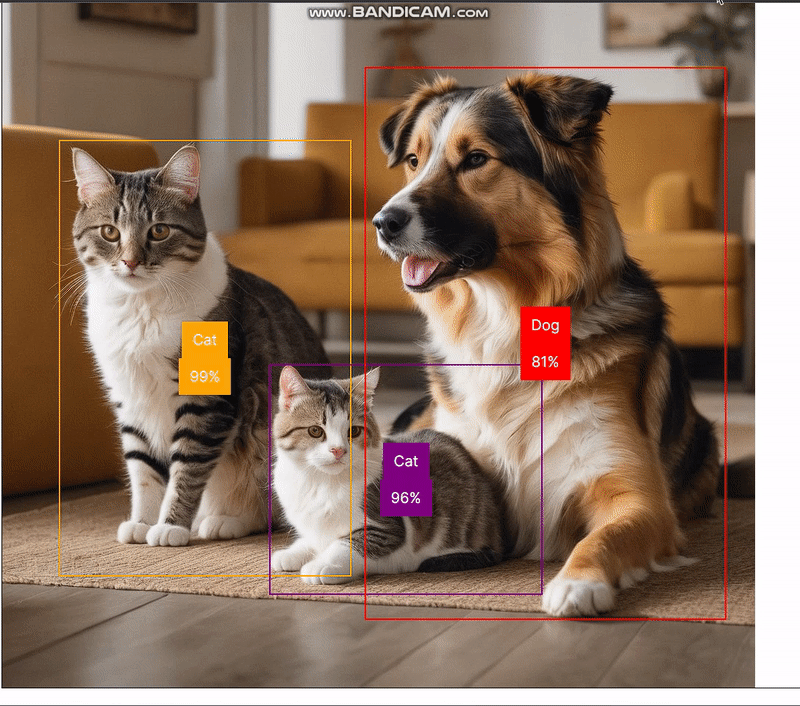
在摄像头上运行物体检测器模型
在本节中,我们将创建一个组件,利用摄像头的视觉数据运行物体检测。为了访问系统网络摄像头,我们将安装一个新的依赖项 React-webcam:
npm i react-webcam
使用 React-webcam 访问可视数据
要使用 React-webcam 软件包访问系统网络摄像头,请在 components 目录下创建一个新文件 CameraObjectDetector.jsx,并添加以下代码:
"use client";
import React, { useRef, useState, useEffect } from "react";
import * as cocoSsd from "@tensorflow-models/coco-ssd";
import Webcam from "react-webcam";
const CameraObjectDetector = () => {
// Use useRef to handle webcam
const webcamRef = useRef(null);
// Use useRef to draw canvas
const canvasRef = useRef(null);
// Handle predictions
const [predictionsData, setPredictionsData] = useState([]);
// Intialize cocoSsd
const initCocoSsd = async () => {
const model = await cocoSsd.load();
setInterval(() => {
detectCam(model);
}, 5);
};
// Function to use webcam
const detectCam = async (model) => {
if (
webcamRef.current !== undefined &&
webcamRef.current !== null &&
webcamRef.current.video.readyState === 4
) {
// Get video properties
const video = webcamRef.current.video;
const videoWidth = webcamRef.current.video.videoWidth;
const videoHeight = webcamRef.current.video.videoHeight;
// Set video width and height
webcamRef.current.video.width = videoWidth;
webcamRef.current.video.height = videoHeight;
// Set the canvas width and height
canvasRef.current.width = videoWidth;
canvasRef.current.height = videoHeight;
// Detect objects in the image
const predictions = await model.detect(video);
console.log(predictions);
// Draw canvas
const ctx = canvasRef.current.getContext("2d");
}
};
// useEffect to handle cocoSsd
useEffect(() => {
initCocoSsd();
}, []);
return (
<div
style={{
height: "100vh",
display: "flex",
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center",
}}
>
<Webcam
ref={webcamRef}
style={{
position: "relative",
marginLeft: "auto",
marginRight: "auto",
left: 0,
right: 0,
textAlign: "center",
zindex: 9,
width: 640,
height: 480,
}}
/>
<canvas
ref={canvasRef}
style={{
position: "absolute",
marginLeft: "auto",
marginRight: "auto",
left: 0,
right: 0,
textAlign: "center",
zindex: 9,
width: 640,
height: 480,
}}
/>
</div>
);
};
export default CameraObjectDetector;
在上面的代码块中,我们集成了 React-webcam,以返回检测到的系统网络摄像头捕获的视频片段。我们还将这段视频传递给 cocoSsd 模型,并在此基础上记录预测结果。在接下来的章节中,我们将使用这些预测数据在 canvas 元素中创建边界框。要加载该组件,请对 app/page.jsx 进行以下更改:
import CameraObjectDetector from "@/components/CameraObjectDetector";
import ImageDetector from "@/components/imagedetector";
export default function Home() {
return (
<div>
{/* <ImageDetector /> */}
<CameraObjectDetector />
</div>
);
}
现在,如果我们运行应用程序,就会在浏览器中得到如下结果:

在控制台中,我们可以看到 cocoSsd 的预测结果:

在上图中,记录的预测值包含 bbox, class, 和 score 值。
绘制边界框
为了绘制边框,我们将创建一个名为 drawBoundingBox 的函数,该函数将接收预测结果,并使用这些数据在视频中的对象上构建矩形。
// An array of bounding box colors
const colors = ["blue", "green", "red", "purple", "orange"];
// Shuffle the array to randomize the color selection
function shuffleArray(array) {
for (let i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
[array[i], array[j]] = [array[j], array[i]];
}
}
shuffleArray(colors);
// Counter to keep track of the next color to use
let colorCounter = 0;
// Draw bounding boxes
const drawBoundingBox = (predictions, ctx) => {
predictions.forEach((prediction) => {
const selectedColor = colors[colorCounter]; // Use the next color from the array
colorCounter = (colorCounter + 1) % colors.length; // Increment the counter
// Get prediction results
const [x, y, width, height] = prediction.bbox;
const text = prediction.class;
// Set styling
ctx.strokeStyle = selectedColor;
ctx.font = "40px Montserrat";
ctx.fillStyle = selectedColor;
// Draw rectangle and text
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.fillText(text, x, y);
ctx.rect(x, y, width, height);
ctx.stroke();
});
};
在上面的代码块中,我们创建了一个颜色数组,用于边界框。通过 predictions 状态,我们可以访问 bbox 属性来获取对象的尺寸,并访问 class 属性来对显示的对象进行分类。接下来,我们使用 canvas prop ctx 为边界框绘制矩形和文本。
最后一步,我们将把画布属性和预测值传递给 detectCam 中的 drawBoundingBox 函数:
const detectCam = async (model) => {
if (
webcamRef.current !== undefined &&
webcamRef.current !== null &&
webcamRef.current.video.readyState === 4
){
//... Former code here
// Draw canvas
const ctx = canvasRef.current.getContext("2d");
drawBoundingBox(predictions, ctx);
}
};
现在,当我们运行应用程序时,就能在视频上看到边界框了:

小结
本文探讨了如何在网络应用程序中集成对象检测功能。我们首先介绍了对象检测的概念及其有益的应用领域,最后使用 React.js 和 Tensorflow 在网络上创建了对象检测的实现。
使用 Tensorflow 进行对象检测的功能是无限的。它的其他自定义模型可以进一步探索这些功能,为监控、增强现实系统等现实世界场景创建交互和应用。






评论留言